Compressors for direct current
Compressors for direct current
Comfort is becoming more and more important these days - also in refrigeration technology. This applies in particular to the field of mobile refrigeration technology, from mobile cool boxes with compressor technology to vehicle cabin cooling for trucks. For this reason, today we are dealing with compressors for direct current and mobile use.
Compressor with EC motor
There are two main points that are particularly important for compressors in mobile applications: First, the mechanical suitability for use in non-stationary applications such as mobile homes, trucks, boats and coolers. Since the mechanical loads on a compressor - for example in a truck - are much higher than in stationary operation, the compressors must be designed for this (types "BD" = battery driven). For example, the internal suspension and various internal parts of BD compressors are mechanically reinforced so that they are resistant to changing centrifugal forces, road bumps, etc. On the other hand, the direct current supply plays a decisive role. In most mobile applications, the on-board electronics work on a direct current basis.
Different speeds
Because of this, the electronics of BD compressors differ significantly from stationary compressor starting devices designed for AC. In the case of compressors for direct current, the current direction of the supply voltage - in contrast to alternating current - is always the same and does not change. A rotating field must therefore be generated electronically. In other words: a BD compressor basically requires electronics for operation, so it makes sense to equip them with additional features. This includes the possibility of being able to operate the compressor at other speeds.
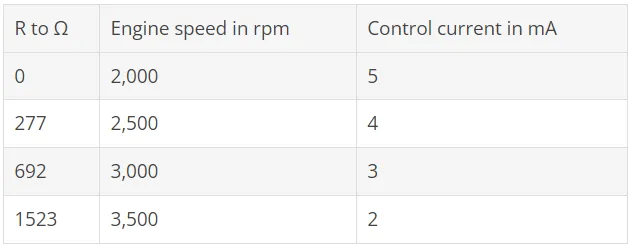
The standard speed of a BD compressor is 2000 rpm (an AC compressor rotates about 2900 rpm with one pole pair and 50 Hz). With most BD compressors, however, the speed can easily be increased up to 3500 (in some types even up to 4500 rpm). For this purpose, a resistor is connected between the "C" and "T" terminals of the electronics.
Depending on the resistance value, the desired speed can be defined. The resistor can simply be selected as a standard resistor approximately the size of the resistor value table in the BD brochure. The fact that the compressor then runs at 2511 revolutions per minute instead of 2500, for example, is irrelevant in practice. As the compressor speed increases, so does the refrigeration capacity, since the compressor then passes through more volume – or the volume flow increases.
Due to this fact, it is possible under certain circumstances to use a smaller BD type as a service replacement for a slightly larger compressor by increasing the speed slightly. The 2 cm3 compressor BD 35F with a speed of a good 2500 rpm can be used as a replacement for a BD 50F with 2.5 cm3 at 2000 rpm.
battery protection shutdown
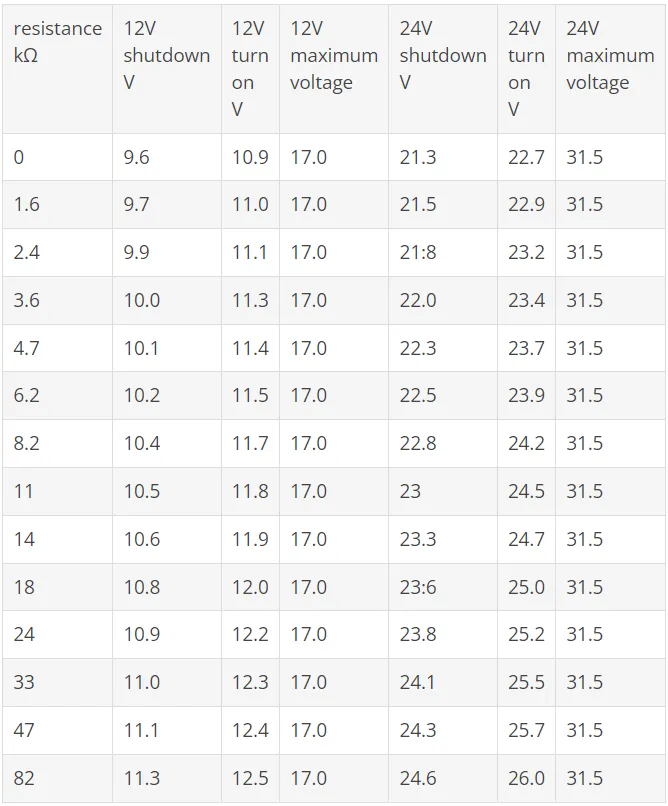
In stationary refrigeration systems that are operated at the socket, an undervoltage protection switch-off is not common and would only make sense in exceptional cases. The situation is completely different with dc compressors. It would be extremely annoying if a luxury class car could no longer start due to a dead battery, just because the BD compressor for the cooling compartment in the rear seat bench drained it completely. To prevent this, the standard BD electronics are equipped with a battery protection shutdown function.
This is the "factory setting" at 9.6 V as the switch-off value and 10.6 V as the switch-on value for on-board voltages of 12 V. Since these values are already quite low, they can be changed with resistors - similar to the procedure for speed preselection. The path of the protective shutdown resistor is between “C” (“common”) and “P” (“protection”). This means that higher switch-off values can also be achieved, ie the battery can be discharged to a lesser extent. In the case of special electronics, such as for solar use, this function is usually removed, since a photovoltaic panel supplies different voltages, including undervoltages, without there being "imminent danger".
thermostat
With DC compressors, the cooling command can be connected directly to the electronics. For this purpose, a potential-free contact must be connected between contacts "C" and "T" (thermostat). A simple thermostat (fridge thermostat or KP thermostat) should be provided here. As soon as the compressor is to be switched on, the thermostat switches through. When the desired temperature is reached, for example in the cool box, the thermostat contact opens and the compressor stops. There are no special requirements in terms of contact loading for these thermostats, as they are not integrated into the load circuit. In general, however, the ampere values in a car / truck are always quite high, since the voltage used is much lower than in the stationary area and the current must therefore be correspondingly higher.
diagnostic function
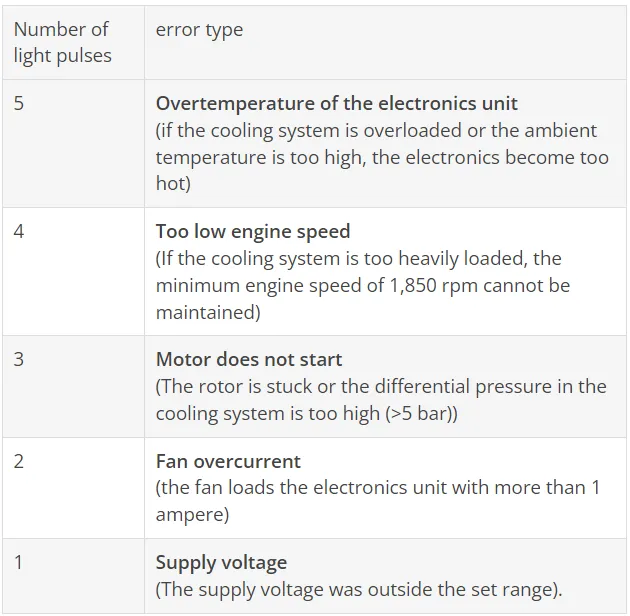
A diagnostic function is integrated into the compressor electronics to facilitate service and commissioning. This function distinguishes between 5 different error diagnoses: "Battery protection shutdown", "Fan overcurrent", "Starting with back pressure", "Minimum speed" and "Electronics overtemperature". "Battery protection shutdown" means that the battery protection voltage has fallen below - or the restart voltage of the battery protection has not yet been reached. This means that the compressor must not be started so that the weakened battery is no longer discharged. "Fan overcurrent" means that the fan connected to terminals "+" and "F" is drawing too much current (more than 1A). A 12 V device must always be selected as the fan - regardless of whether the BD compressor is operated on a 12 or 24 V on-board network. In the case of "Starting with back pressure", the diagnostic function tells us that a back pressure in the refrigeration system of more than 5 bar difference between the suction and pressure side prevents the compressor from starting. Complete pressure equalization in the system is ideal for starting up a DC compressor, but even small pressure differences can be overcome during start-up. In extreme cases, this error code can also mean that there is a mechanical defect in the compressor that prevents it from starting (eg seizures in the crankshaft bearing). This error code will also appear without a measurable differential pressure upstream and downstream of the compressor. Another error code is "Underrun minimum speed". This code is issued when too high a load (e.g too high pressure level on the pressure side) acts on the compressor and pushes the speed to below 1850 rpm. The last possibility of fault diagnosis is "Electronics overtemperature". Especially in mobile applications in very small compartments or in the engine compartment in summer, high temperatures can occur in the electronics unit. To protect this unit, it may be necessary to switch it off if the thermal stress is particularly high. These 5 diagnoses are output as an interval signal. If an LED is connected to the BD electronics, the error code can be read directly from the flashing signal. Error code 3 (starting with back pressure) is indicated by three flashes, then a pause, three more flashes, etc. If no LED is connected, the interval impulses between the contacts "+" and "D" (diode) can be measured using a multifunction measuring device (position >24 V dc). Then, for example, two short pulses - pause - two short pulses - pause etc. would be error code 2, i.e. "fan overcurrent".
Compressor cooling and assembly
BD compressors are basically single-cylinder machines with a vertically arranged crankshaft. They are normally supplied with sufficient oil so that an oil additive is generally not necessary. Due to the additional heat radiation, the compressors have oil centrifugal cooling. Static cooling by the ambient air is usually sufficient for the small power sizes, cooling by forced ventilation is necessary for the larger compressors or high evaporation temperatures. For this reason, these compressors should not be equipped with a sound insulation hood. A look at the respective data sheet provides information as to whether static cooling ("S") is sufficient or whether forced ventilation ("F" fan = fan) must be used. The soldered connections of these compressors are sealed with capsolutes in order to avoid unnecessary entry of foreign particles or moisture into the compressor. To remove these capsolutes, there are special capsolute lifters that should be used to open all closures. This means that even if the process socket is not required, it must be freed from the capsolute and soldered shut.
The compressors are mounted on rubber buffers. These mounting rubbers should always be used, as the buffering, together with the internal suspension springs of the inner compressor block, absorbs the forces when the compressor starts and stops, centrifugal forces and vibrations.
Comparison of technologies
As an alternative to compression refrigeration systems for mobile direct current operation, two other technologies are mainly widespread: cooling using a Peltier element and absorption refrigerators. Peltier elements are attractively priced, but offer only very low cooling capacities compared to BD compressor systems. They are often installed in simple and smaller coolers for private use. Their use is also limited with regard to the maximum differential temperature. An evaporation temperature in the minus range at an outside temperature of 30°C is not feasible with a Peltier element - but with BD technology it is. In terms of energy, the compressor technology in the direct current range is significantly more efficient - not least because of the EC motor technology. As a rule of thumb, only about 1/3 of the power consumption can be assumed here, which a corresponding Peltier element would consume. In terms of energy, the absorption refrigerator is on a similar level to the Peltier element. It also consumes three times more electricity than compressor cooling. Absorption refrigerators are available as minibars in hotels and - as a mobile application - often in mobile homes. The absorption refrigerators in campers are usually operated using a heat source (usually propane burners).