Main valves and pilot valves in refrigeration systems "ICS" main valves
construction
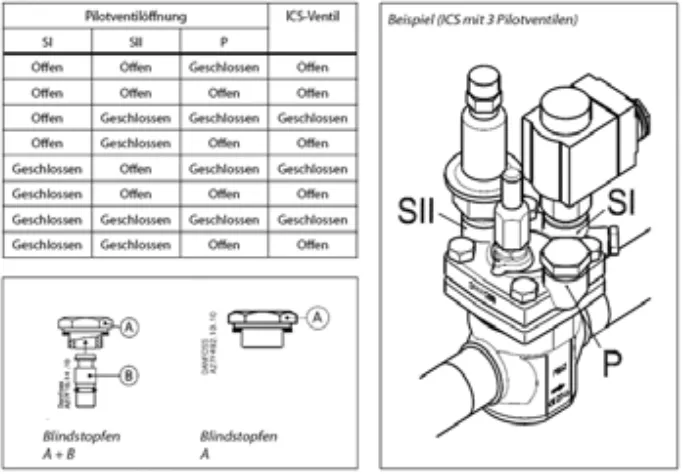
"ICS" main valves are available in the "1 Pilot" and the "3 Pilot" versions. In the "1 Pilot" version, a pilot valve can be screwed directly onto the main valve, whereas in the "3 Pilot" version, up to three pilot valves can be mounted on the main valve. With the "1 Pilot" version, a single function can be controlled, such as the evaporation pressure or the condensing pressure. The "3 Pilot" - "ICS" can do even more. It has two pilot ports connected in series and another pilot port connected in parallel with each other. The series or series connections are labeled "S1" and "S2" for "series". The "P" terminal stands for "parallel" and is also connected in parallel with "S1" and "S2". Thus, circuit variants such as condensing pressure control with additional forced opening or forced closing are possible. Should the number of pilot connections not be sufficient due to a particularly complex circuit, an almost infinite number of circuit options can be created by means of external pilot housings and pilots mounted thereon in external pilot lines. To facilitate commissioning, "ICS" main valves offer the possibility of manual override. The main valve can be opened by hand with the hand spindle attached to the center of the valve head. In any case, this manual spindle should be returned to the starting position for normal operation (counterclockwise until it stops). The "ICS" main valve consists of a housing body, which is soldered directly into the pipeline (or welded, in the case of ammonia as a refrigerant). In this body, a functional module is used, which can be easily replaced in case of service, without the pipe connections are affected. When designing main valves, care must be taken that they are servovalves requiring a minimum pressure drop. Although this is very low, which means a very good partial load capacity, but still not negligible. If, in an application such as deep-freezing, a valve without a minimum pressure drop is actually needed, this is possible with the "ICS" and external control by means of a higher pressure. For this purpose, an external pilot connection can be mounted on the "ICS". The valve, which is mounted in the suction line is opened by the hot gas or cold gas pressure which is introduced by a control line. Equipped with: "icS" "3 Pilot" version, external connection to "S1", "eVM" to "S2" and blind plug "A + B" to "P". Alternatively, a "PML (X)" can be used as a special main valve for this exact application.

Solenoid valve function
The simplest application of a main valve is the solenoid valve function. In this function, the "1 pilot" version of the main valve is equipped with an "EVM" pilot valve. This pilot valve can be screwed directly onto the main valve. "Nc" (normally closed) is the most common application for solenoid valves and means that the solenoid valve is closed when de-energized. The pilot valve "EVM" in nc version is suitable for this purpose. If now the coil of the "EVM" (nc) is energized, then opens the pilot valve. This opens the internal control channel in the "ICS" between the valve inlet and the internal pressure chamber above the "ICS" power piston, so that the higher pressure flows from the inlet of the main valve into the pressure chamber above the power piston and pushes it downwards. This will open the main valve. During the closing process, the channel is closed by the "EVM" and the higher pressure above the power piston is relieved by a small bore to the outlet of the valve. With opposite direction of action an "EVM" (no) can be used ("no" stands for "normally open", ie "normally open"). "EVM" (no) pilot valves differ from "EVM" (nc) in addition to the sense of direction in that a slightly stronger coil (12 W in AC insert) is used and an additional groove is pressed into the lower part of the anchor tube.

Evaporation pressure control
Evaporative pressure regulators are mounted, for example, in multi-evaporator systems behind the evaporator, which is to be operated at a higher pressure level than the other evaporators. Often one finds also in chillers a evaporation pressure regulator as additional security against the freezing of the water in the evaporator. Evaporative pressure regulator for larger power is a main valve with screwed pilot valve "CVP 7". Two low-pressure gauges are ideal for setting the set point below which the valve will accumulate (valve closes) and above which it will pass the refrigerant (valve opens). one is connected to the suction port of the compressor and the other one serves to indicate the pressure between evaporator and evaporation pressure regulator. This second manometer can be connected to the service connection of the "ICS", since a 7/16 "UnF measuring connection can be retrofitted to the manometer connection on the input side of this component. now the setpoint can be adjusted directly at the "CVP". Turning clockwise (in the "+" direction) will increase the setpoint, while turning it counterclockwise (in the "-" direction) will reduce the setpoint. Increases the pressure drop by setting the setpoint while the system is running, it is sufficient to set the desired input pressure on the controller. if only one nD manometer is available for measuring the evaporation pressure and if the increase in the setpoint to the desired value results in a correspondingly higher evaporation pressure when the system is running, the controller is set correctly. Caution with actual evaporating pressure values that are higher than the desired set point: an immediate setting is not possible without further ado, as the controller now basically opens at all setpoints that are below the actual values. in such a case, the evaporation pressure must first be lowered. This is possible, for example, in a forced-ventilated evaporator by switching off the fan. after setting the "CVP" the fan should be started again. With main valves can also be realized a switching of two different evaporation temperatures. Thus, by turning on and off the "EVM" and using a "3 pilot" main valve,

Head Pressure Control
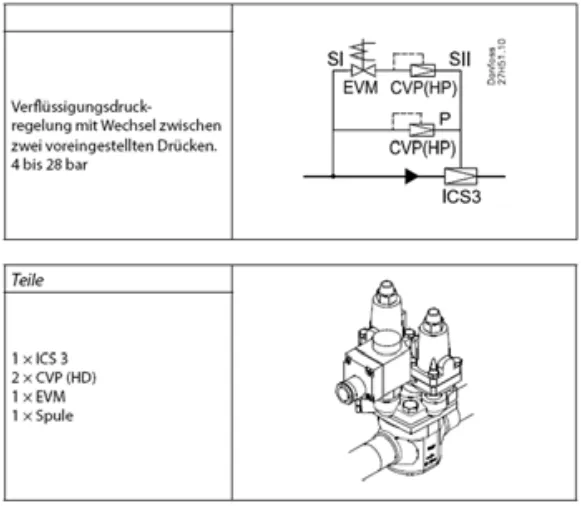
Condensing pressure regulators are used to prevent the condensation temperature from falling too low in a refrigeration system, especially in the cold season. For installation, the hot gas line in the flow direction after the T-piece outlet to the collector pressure regulator or the condensate line are suitable. When installing in the hot gas line, the check valve in the condensate line must under no circumstances be dispensed with, since otherwise the refrigerant can flow from the rear into the cold liquid and the desired effect of rapid pressure build-up in front of the expansion valve does not occur even in winter. The most commonly used variant is the installation of the condensing pressure regulator in the condensate line (between condenser and collector). The higher pressure condensing pressure regulator is almost identical to the evaporative pressure regulator. It is a main valve "ICS" (or "PM") with screwed pilot valve "CVP 28" or "CVP 22" for R134a. The number after the "CVP" stands for the maximum control pressure of the pilot valve, here 28 bar or 22 bar. It is not surprising that the required components for the evaporation and evaporation pressure control are similar, but in both cases a certain minimum pressure is defined, which should not be undercut. Only the total pressure situation is different in both cases. For adjustment, at least one high-pressure gauge should be connected to the input-side pressure gauge connection of the "ICS" (pressure gauge connection is available as accessory for "ICS" and, if necessary, retrofitted). Optimal is the additional connection of a high pressure gauge to the collector. The further procedure is identical with the evaporation pressure regulator "CVP". it is ideal if the condensing temperature is significantly lower than the desired set point when operating the system with "relaxed" "CVP" (very low setpoint). When increasing the pressure (use of a hD manometer), or significantly increasing the pressure drop by setting a higher set point (use of two HD manometers), the desired setpoint can be set directly here. If the pressure level on the high-pressure side is too high, for example, the commissioning can be moved from a particularly hot day to a cooler one. Another possibility is z. B. For a compressor network, operate a maximum of one compressor during the adjustment of the delivery pressure regulator. In difficult cases, lowering the pressure level on the LP side - as described in the chapter "Evaporative pressure regulator" - may be useful. By such a measure, the pressure level is usually lowered on the high pressure side as well. Here as well, a switchover can be realized between two different liquefaction temperatures, as in the case of evaporation pressure. This is feasible with a "3 pilot" main valve, two "CVP" set at different condensing temperature levels and one "EVM" pilot. In difficult cases, lowering the pressure level on the LP side - as described in the chapter "Evaporative pressure regulator" - may be useful. By such a measure, the pressure level is usually lowered on the high pressure side as well. Here as well, a switchover can be realized between two different liquefaction temperatures, as in the case of evaporation pressure. This is feasible with a "3 pilot" main valve, two "CVP" set at different condensing temperature levels and one "EVM" pilot. In difficult cases, lowering the pressure level on the LP side - as described in the chapter "Evaporative pressure regulator" - may be useful. By such a measure, the pressure level is usually lowered on the high pressure side as well. Here as well, a switchover can be realized between two different liquefaction temperatures, as in the case of evaporation pressure. This is feasible with a "3 pilot" main valve, two "CVP" set at different condensing temperature levels and one "EVM" pilot.

Home control
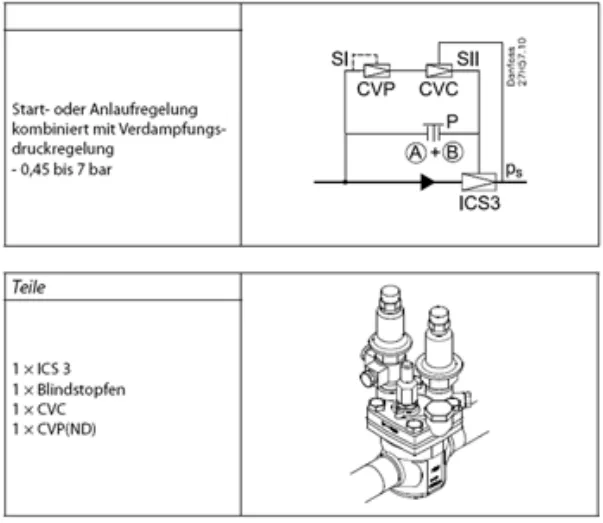
A starting control is appropriate when the compressor of the system - often a freezer compressor - is to be protected from excessive pressure. The installation takes place in the suction line. lately, the starter controls have been slightly outdated by individually and electronically adjustable MOP points with electronic injection control. Nevertheless, they continue to assert themselves as classics of pressure control. For larger capacities, we recommend a main valve "ICS" (or "PM") with pilot valve "CVC" screwed on. On the "CVC" pilots, after the main valve, a stub pipe must be brought in the direction of flow from the main line. Thus, the actual value of the pressure variable to be controlled between the valve and the compressor is supplied to the start regulator. The adjustment of a start regulator is no problem when the system is running if the evaporation temperature is above the desired set point. The "CVC" does not require a separate metering port as the compressor intake manifold is generally equipped with one. This measuring connection is used for adjustment. Again, the procedure is similar to the "CVP" variants - but in the opposite way. This means that if the suction pressure upstream of the compressor is lowered directly by pressing the "CVC" while the system is running and can be set to the desired setpoint, the device is already ready for operation. This becomes even clearer when another low pressure gauge z. B. is connected to the evaporator outlet. This shows that there would be no pressure drop without "CVC" and that with the adjusted value there is a pressure drop to the desired setpoint. The problem is only very low suction pressures before the setting of the start regulator, but for which there is a simple solution. Since it is usually freezing in such a case, z. B. the defrost heater can be used to increase the suction pressure. Another possibility is that the TC room heats up to higher temperatures than during operation. This is normally not a problem during the construction phase. For main valves, combinations of different functions are possible. For example, to combine start and evaporative pressure control, it is sufficient to connect in series the pilot valves "CVP" and "CVC" on ports "S1" and "S2" on the main valve. Thus, both the evaporation pressure is kept constant and prevents exceeding the maximum suction pressure.
Power control (hot gas bypass control)
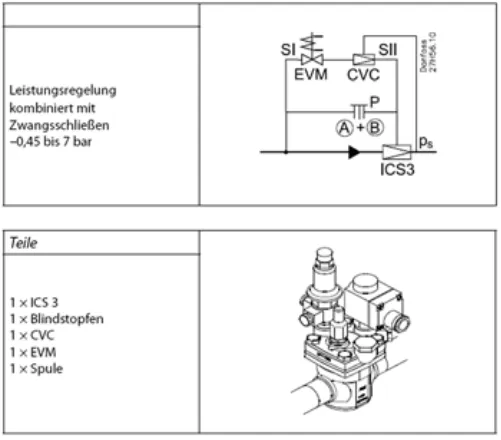
Capacity controllers are often used in systems in which phases of the partial load are to be compensated automatically. This is based on the principle that the suction pressure drops when the heat input into the evaporator is less than at full load. That is, the target value of a hot gas bypass controller is set slightly below the suction pressure at full load in the steady state. If the suction pressure now drops, the ratio of compressor to evaporator cooling capacity shifts in favor of the compressor, the capacity regulator opens and allows hot gas to flow from the high-pressure side to the low-pressure side. This prevents a further decrease in the suction pressure. The investment costs for such a power control are low compared to a compound controller plus pressure sensor and compressor network. Thus, in the latter case, a similar effect of the suction pressure stabilization is achieved by switching on and off of compressors. A disadvantage of the hot gas bypass control is the energy aspect. In principle, a distinction is made between two types of hot gas bypass control: systems with an evaporator is a bypass control in the injection line (between expansion valve and evaporator), in Mehrverdampferanlagen to the hot gas bypass in the suction line, which is usually provided a post-injection for desuperheating the refrigerant , For larger outputs, a main valve "ICS" (or "PMC") with screwed-on pilot valve "CVC" is the right choice for both applications. To set the hot gas bypass regulator, an nD pressure gauge is required. ideal for the control process is an evaporation pressure below the setpoint. In this case, the bypass controller can be set directly to the desired value. The flow noise is a clear indicator of whether a bypass is being used or not. If the evaporation pressure is too high, the same procedure applies as described in the section "Evaporating pressure regulator". a small note to the post-injection valve, if the bypass should go directly into the suction line. There are classic post-injection valves whose sensors are mounted on the pressure side of the compressor. but it can also normal expansion valves with internal pressure compensation to Nacheinspritzventilen be converted. To do this, only the superheat setting must be adjusted upwards and the sensor mounted on the suction side in front of the compressor. A practicable fist value is 15 k. Thus, the Nachspritzventil does not interfere with the normal injection valve and still ensures that the compressor is not too high intake temperatures. Very useful with a power controller is the forced closing function. This is equipped with an "EVM" pilot valve, which is connected in series with the "CVC" pilot valve (both pilots on "S1" and "S2"), and a blind plug on connection port "P" with only one "icS" realizable. The blind plug is available in two versions: version "A", in which it only represents a degree to the outside and version "A + B", in which it also closes the internal channels. Very useful with a power controller is the forced closing function. This is equipped with an "EVM" pilot valve, which is connected in series with the "CVC" pilot valve (both pilots on "S1" and "S2"), and a blind plug on connection port "P" with only one "icS" realizable. The blind plug is available in two versions: version "A", in which it only represents a degree to the outside and version "A + B", in which it also closes the internal channels. Very useful with a power controller is the forced closing function. This is equipped with an "EVM" pilot valve, which is connected in series with the "CVC" pilot valve (both pilots on "S1" and "S2"), and a blind plug on connection port "P" with only one "icS" realizable. The blind plug is available in two versions: version "A", in which it only represents a degree to the outside and version "A + B", in which it also closes the internal channels.
Collectors pressure control
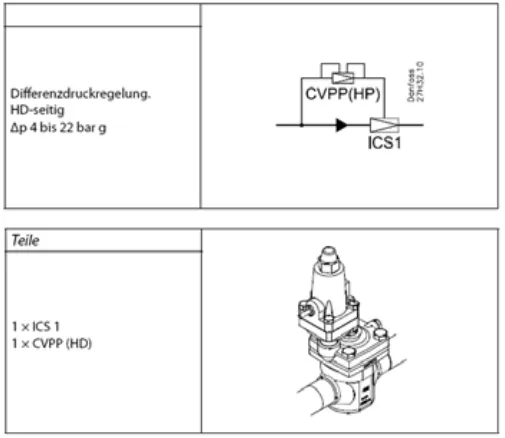
Header pressure control is typically used in combination with positive pressure control. a collector pressure regulator is needed on the one hand for the bypass of the condenser at system start in winter and on the other hand to close the bypass when the operating state is reached again. With this measure, a rapid pressure build-up in front of the expansion valve - even with cold outside temperatures - ensured, unwanted system shutdowns via the low pressure switch are avoided. Danfoss offers "ICS" (or "PM") main valves with differential pressure pilot attachment "CVPP" for greater performance. With "icS" with "CVPP", the differential pressure can be set, which can be set as desired. The correct "CVPP" setting should best be made during winter operation. For this purpose, the refrigeration system is first put into operation and then waited until the pressure has built up on the high pressure side. The condensing pressure regulator is still closed. The difference between the high and collector pressures is high during the startup process. This initially flows the refrigerant through the bypass to the collector. a practicable fist value for setting the "c VPP" is 1.5 bar. Turning clockwise increases this value as needed.
Differential pressure control
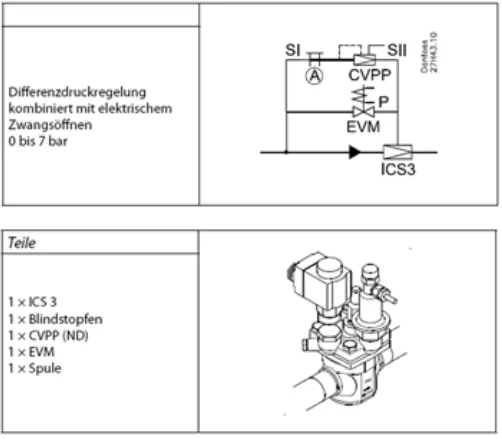
In addition to the collector pressure control, there is another application for the regulation of the differential pressure. This concerns systems with Heißgas Abtauung, since here the hot gas must flow in the Abtaufall through the evaporator in the direction of liquid line. In this case, this "artificial" differential pressure in operating phases without defrost should be switched off. For this case we recommend the use of an "ICS" (or "PM") main valve with differential pressure pilot attachment "CVPP", as previously mentioned. In order to switch off the differential pressure control not required in the collector control mode, another pilot is required: an "EVM" solenoid valve for direct mounting on "ICS" (or "PM"). If the two pilot valves "CVPP" (stub line to the main line downstream of the valve is not forgotten) and "EVM" parallel to an "ICS" for max. mounted three pilot valves, then the differential pressure function of the "CVPP" is active when the "EVM" is closed. When the "EVM" is open, no (increased) differential pressure is driven. For closing a main valve "icS" with "CVPP" and "EVM" close the solenoid valve "EVM". Be careful, because there are these pilot valves both normally closed (nc), as well as normally open (no). Thus, for example, a normally closed "EVM" would be closed when the coil is not energized. Then, with the system running, the differential pressure can be set directly after the two high-pressure manometers have been connected in front of and behind the control valve. As a measuring point in the flow direction upstream of the valve, the compressor pressure port, or better still, the lateral pressure gauge port on the "ICS" valve (always valve inlet pressure) can be used.